The Ecological Importance of Lakes in the UK
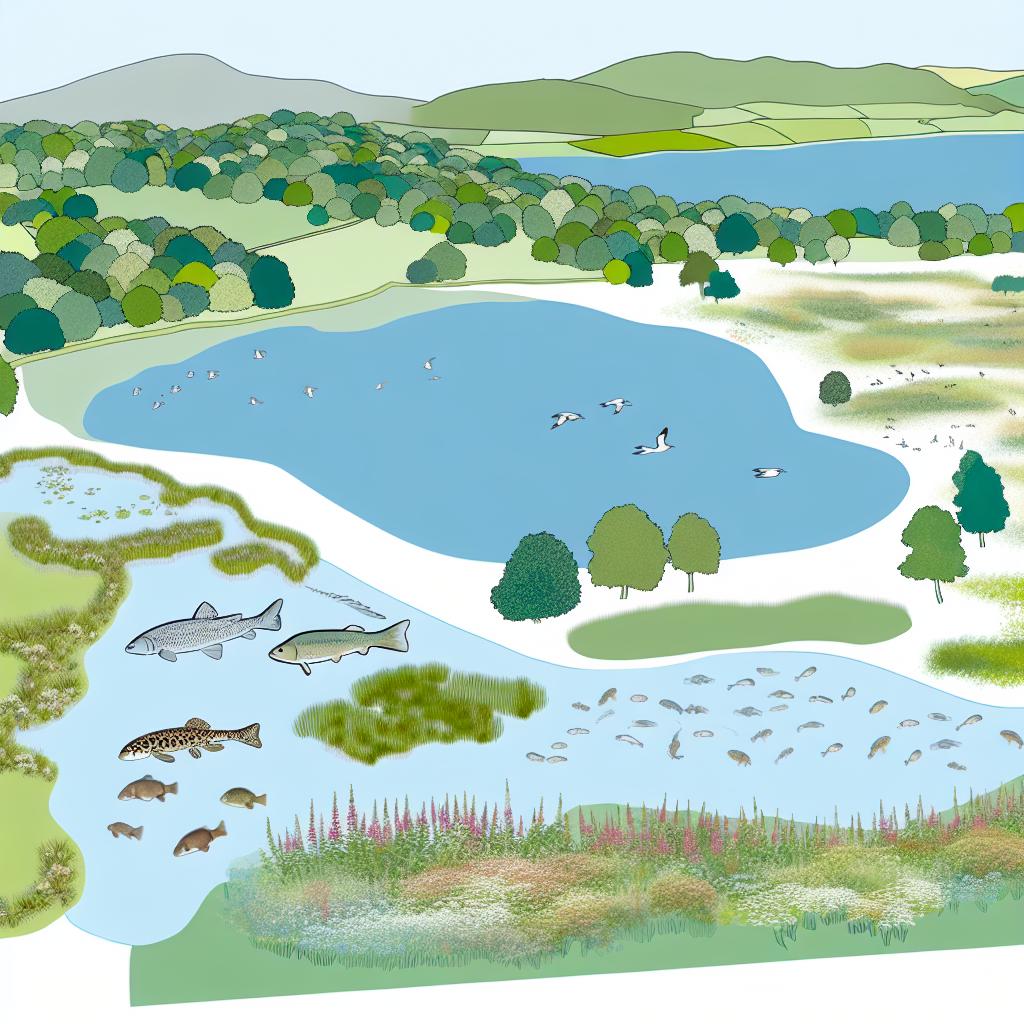
In the United Kingdom, lakes are a crucial part of the country’s ecosystems, serving as vital habitats for a diverse range of flora and fauna. These bodies of fresh water play a key role in supporting biodiversity, influencing climate, and contributing to the overall health of the environment.
Habitat for Biodiversity
Lakes in the UK provide essential habitats for many species. They are home to various fish, including pike, perch, and trout, which are important both ecologically and recreationally. Furthermore, lakes support significant populations of aquatic plants such as water lilies and reeds, which in turn provide shelter and breeding grounds for numerous invertebrates and birds.
Bird species such as the great crested grebe and kingfisher are frequently found around lakes, benefiting from the rich food resources available. Additionally, many amphibians and mammals, like frogs and otters, rely on the aquatic and surrounding terrestrial environments that lakes provide.
The Role of Fish and Aquatic Life
The presence of fish like pike, perch, and trout is pivotal not only for maintaining the ecological balance but also for supporting the recreational fishing industry. These fish contribute to the food web by serving as both predators and prey. Their interactions with other aquatic life forms create a dynamic equilibrium essential for a thriving ecosystem.
Aquatic plants within these lakes, such as water lilies and reeds, play a crucial role in providing cover for smaller fish and invertebrates. This vegetation also aids in stabilizing the lake’s sediment, thus reducing erosion and maintaining water clarity, which is beneficial for plant growth and fish habitats.
Bird Life and Terrestrial Connections
Lakes attract a variety of bird species, with the great crested grebe and kingfisher being particularly noteworthy. Their presence is indicative of a healthy lake ecosystem, as these birds are reliant on vibrant aquatic life for sustenance. The proximity of lakes to other terrestrial environments, such as forests and grasslands, allows for diverse interactions and provides a mosaic of habitats ideal for various life forms.
Contribution to Climate Regulation
Lakes influence local and regional climates by acting as heat sinks. During warmer months, they absorb heat, while in cooler periods, they release it slowly. This moderating effect helps stabilize the microclimate around lake areas, which can impact agricultural productivity and the survival of certain species.
Moreover, the process of photosynthesis by aquatic plants contributes to carbon sequestration. By absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, lakes play a role in mitigating the effects of climate change.
Microclimate Stability
The interaction between lakes and their surrounding atmosphere is crucial in determining local weather patterns. By absorbing heat, lakes tend to reduce temperature extremes, which in turn provides a more stable environment for surrounding agriculture and wildlife. This capability is important for areas that rely heavily on agriculture, as it affects crop yields and growing seasons.
Carbon Sequestration and Ecosystem Services
Through photosynthesis, aquatic plants not only produce oxygen but also remove carbon dioxide from the air, a process that contributes positively to carbon sequestration. This means lakes are continuously working to counteract some of the adverse impacts of human-induced carbon emissions, reflecting their importance beyond immediate ecological boundaries.
Water Quality and Hydrological Role
Lakes contribute to water purification by trapping sediments and filtering pollutants through natural processes. Many UK lakes are fed by rivers, meaning that they serve as an intermediary stage in the hydrological cycle, controlling flood risks by acting as natural buffers during periods of heavy rainfall.
The role of lakes in water regulation is essential not just for wildlife, but also for human populations that rely on these bodies of water for resources, recreation, and aesthetic value.
Natural Filtration Processes
The natural ability of lakes to act as filtration systems is significant in maintaining water quality for both human and ecological needs. Lakes filter pollutants and sediments, ensuring that downstream ecosystems and human communities have access to cleaner water. This natural filtration is a cornerstone of the ecosystem services they provide.
Flood Control and Water Regulation
By acting as reservoirs during periods of high rainfall, lakes help mitigate the impacts of potential floods. This capacity for water retention ensures that sudden climatic events do not lead to catastrophic flooding, protecting both natural and human settlements downstream.
Research and Conservation Efforts
The significance of lakes has not gone unnoticed, with numerous studies and conservation projects aimed at preserving these ecosystems. Organizations such as the WWF UK and RSPB work to raise awareness and protect crucial habitats found in and around lakes.
Efforts to monitor water quality, control invasive species, and restore native vegetation are ongoing. Community involvement in conservation activities, such as clean-up days, further highlights the importance of protecting these vital ecosystems.
Ongoing Research and Monitoring
Continual scientific research plays a pivotal role in understanding the complexities of lake ecosystems. By monitoring ecological parameters, scientists can detect changes in water quality, biodiversity, and climate impacts, facilitating informed conservation strategies. This research is vital in predicting how lakes might respond to future environmental changes.
Public Involvement and Education
The engagement of local communities in conservation activities, such as cleanup events and educational workshops, is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. Increased public awareness and involvement contribute to a cultural ethos that values the protection and sustainable use of natural resources.
Conclusion
In summary, lakes in the UK serve as essential components of the natural environment. They provide habitats for numerous species, contribute to climate regulation, and maintain water quality. Continued research and conservation measures are necessary to ensure the health and sustainability of these important ecosystems for future generations.
These efforts, supported by robust research and active community involvement, will be pivotal in safeguarding the ecological integrity of UK lakes, ensuring that they continue to enrich biodiversity, support climate regulation, and provide invaluable ecosystem services. As guardians of these natural treasures, both public and private stakeholders must remain committed to a future where lakes continue to thrive and serve their multifaceted roles in the ecosystem.